Pumping Breast Milk
There may be times when you are not able to feed your baby from your breast or you choose not to feed your baby from your breast. Breast milk pumping removes milk from your breast. You can then store the milk for your baby to drink later.
There are three ways to pump. You can:- Use your hand to massage and squeeze your breast (hand expression).
- Use a handheld manual pump.
- Use an electric pump.
When you first start to pump, you may not get much milk, but after a few days your breasts should start to make more. Pumping can help stimulate your milk supply after your baby is born. It can also help maintain your milk supply when you are away from your baby.
Work with your health care provider or breastfeeding specialist (lactation consultant) to find strategies that work for you. If you need help, ask for help as soon as possible.
When should I pump?
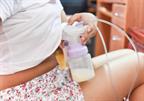 You can start pumping soon after your baby is born. Talk with your provider about when it is best for you to start pumping. Here are some general tips:
You can start pumping soon after your baby is born. Talk with your provider about when it is best for you to start pumping. Here are some general tips:- If you are putting your baby to breast to feed, pump after breastfeeding. This is especially needed if your baby was born early (premature) or has trouble attaching to your breast (latching).
- When you are away from your baby, pump every 2–3 hours for about 15 minutes.
- If your baby gets a bottle feeding, pump around the time your baby gets that feeding.
- If you drank alcohol, wait at least 2 hours before pumping.
- If you are having a procedure with medicine to make you fall asleep so you will not feel pain (anesthesia), talk to your provider about when you should pump before and after the procedure.
How do I prepare to pump?
Try to relax. This makes it easier to stimulate your let-down reflex, which is what makes breast milk flow. To do this:- Look at a picture or video of your baby.
- Smell your baby's blanket or clothes.
- Sit in a quiet, private space.
- Place a warm cloth on your breast. The cloth should be a little wet.
- Gently massage your breast and nipple.
- Play relaxing music.
- Picture your milk flowing.
- Drink water and eat a snack.
What are some tips?
General tips for pumping breast milk

-
Always wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds before pumping. If soap and water are not available, use hand sanitizer.
-
Wear clothes that open in the front or allow easy access to your breasts.
-
Pump both breasts at the same time if you can.
-
If you are not getting very much milk or pumping is uncomfortable, try different pump settings or try using different types of pumps. Talk with your provider or lactation consultant to find strategies that work for you.
-
Pump breast milk directly into clean bottles or other storage containers.
-
Do not use any products that contain nicotine or tobacco. These products include cigarettes, chewing tobacco, and vaping devices, such as e-cigarettes. If you need help quitting, ask your provider.
Tips for choosing a breast pump
The right pump for you will depend on your comfort and how often you will be pumping. When choosing a pump, keep the following things in mind:- A manual breast pump does not need electricity to work. A manual pump is usually cheaper than an electric pump, but can be harder to use. A manual pump may be a good choice if you are pumping occasionally.
- An electric breast pump is usually more expensive than a manual pump, but can be easier to use. An electric pump can also collect more milk than a manual pump.
- A hospital-grade electric pump is recommended if:
- You had a baby who was premature or your baby is sick.
- You will be pumping more than breastfeeding.
- Before buying a pump, check if your insurance will pay for it.
Tips for maintaining a breast pump
- Check your pump's manual for cleaning tips.
- Clean the pump after each use. To do this:
- Wipe down the electrical unit with a dry, soft cloth or clean paper towel. Do not put the electrical unit in water or in cleaning products.
- Wash the plastic pump parts with soap and warm water or in the dishwasher, if the parts are dishwasher safe.
- Let the parts air-dry. Avoid drying them with a cloth or towel.
- For extra protection, sanitize the pump parts at least once each day. This is very important if your baby:
- Was born prematurely.
- Is younger than 2 months old.
- Has a weakened immune system.
- Tubing:
- Breast pump tubing that does not touch the pumped milk does not need to be cleaned regularly.
- If there are water droplets in the tubing when you want to pump, attach the tubing to the pump and turn on the pump. Run the pump until the tube is dry.
- If your tubing is moldy, throw away the moldy tubing and get new tubing.
Contact a health care provider if:
-
You are frustrated with breast milk pumping.
- You have pain or discomfort in your breasts such as:
- Continued pain with breast milk pumping.
- Breasts that are too filled with milk (engorgement) that do not improve after 48–72 hours.
- Cracking or soreness in your nipples that does not get better with treatment.
- Bleeding from your nipples.
- You have signs of an infection, such as:
- A fever.
- Pus-like fluid coming from your nipples.
- Warm, red areas or painful areas on your breasts.
This information is not intended to replace advice given to you by your health care provider. Make sure you discuss any questions you have with your health care provider.

